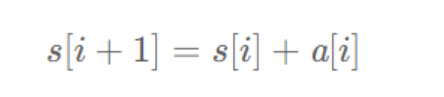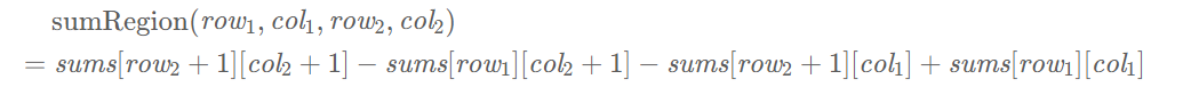0.常用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
boolean ans = Character.isDigit();
boolean ans = Character.isLetter();
Character.isUpperCase(ch)
Character.isLowerCase(ch)
|
1
| int num = Math.ceil(num);
|
1
2
| float f = 123.456f;
String s = String.format("%.2f", f);
|
1
| String str = Integer.toBinaryString();
|
1
| Arrays.sort(nums, i, j);
|
1
| static final int MOD = 1000000007;
|
1
| Arrays.equals(array1, array2)
|
1
| int min = Integer.MIN_VALUE / 2;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| next:
for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < strs.length; j++) {
if (j != i && isSubseq(strs[i], strs[j])) {
continue next;
}
}
return strs[i].length();
}
|
这会导致外层循环继续下一次迭代,而不需要执行内层循环的剩余部分。
增强for
1.数组
1.1知识点:
见二分查找章节
- 快慢指针
- 滑动窗口
- 矩阵题目(主要是模拟,都比较难)
- 循环数组(503):1.再开辟一个数组,拼接到原数组;2.遍历时候按2倍数组遍历,i 取 i % nums.length
1.2用法:
//数组的填充
1
2
| char[] c = new char[n];
Arrays.fill(c, '.');
|
判断两个数组是否相等:
1
| Boolean flag = Arrays.equals(arr1, arr2);
|
数组的自定义排序:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<int[]>() {
public int compare(int[] arr1, int[] arr2) {
return arr1[0] - arr2[0];
}
});
|
数组初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] numbers = new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] numbers = new int[5];
int a[][]={{1,2,3},{4,5,6}};
int[][] ints = new int[4][2];
int[][] arr3 = new int[5][];
|
list的用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
list.clear();
Collections.sort(list);
Collections.sort(list, Collections.reverseOrder());
list.removeLast();
ans.add(path);
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
|
1.3困难题目
矩阵题目全部、34.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置(两次二分,查第一个和最后一个位置)、
2.链表
2.1知识点:
经常需要创造出一个虚拟节点、大部分题目画图模拟即可、合并有序链表(必须快速写)、双向链表(LRU)、链表的归并排序(148)、链表的深拷贝(138)
环形链表:
2.2用法
双向链表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
class DLinkedNode {
int key;
int value;
DLinkedNode prev;
DLinkedNode next;
public DLinkedNode() {}
public DLinkedNode(int _key, int _value) {key = _key; value = _value;}
}
|
2.3困难题
148.排序链表、146.LRU
3.哈希表
3.1知识点
有时候用一个int[26]的数组存储字母可能更好。
3.2用法
map和set除了遍历外的各种时间复杂度为O(1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
hashMap.forEach((key, value) -> {
System.out.println("(" + key + ", " + value + ")");
});
for (Map.Entry <Integer, String> entry: map.entrySet()) {
key = entry.getKey();
value = entry.getValue();
}
Set<String> set = map.keySet();
for(String key : set){
......
}
boolean res = map.containsKey(key);
int res = map.getOrDefault(key, 0);
map.remove(key);
boolean res = map.isEmpty();
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
System.out.println(map.firstKey());
System.out.println(map.lastKey());
System.out.println(map.lowerKey("Bob"));
System.out.println(map.higherKey("Bob"));
System.out.println(map.floorKey("Bob"));
System.out.println(map.ceilingKey("Bob"));
System.out.println(map.subMap("Alice", true, "Charlie", true));
System.out.println(map.headMap("Charlie", true));
System.out.println(map.tailMap("Charlie", true));
System.out.println(map.firstEntry());
System.out.println(map.lastEntry());
System.out.println(map.lowerEntry("Bob"));
System.out.println(map.higherEntry("Bob"));
System.out.println(map.floorEntry("Bob"));
System.out.println(map.ceilingEntry("Bob"));
System.out.println(map.pollFirstEntry());
System.out.println(map.pollLastEntry());
|
自定义排序:类似堆
4.字符串
4.1知识点
前缀和(560.)

4.2用法
string的常用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
char[] charArr = s.toCharArray();
String str = new String(charArray);
String numberStr = "123";
int number = Integer.valueOf(numberStr);
String str = String.valueOf(num);
String text = "This\tis\ta\tsample\tstring";
String[] words = text.split("\t");
String originalString = " Hello, world! ";
String trimmedString = originalString.trim();
str.charAt();
String str = "Hello, World!";
String substr1 = str.substring(7);
String substr2 = str.substring(0, 5);
int result = str1.compareTo(str2);
|
stringbuilder的用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String str = "Hello";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(str);
sb.append("Hello");
sb.insert(5, "beautiful ");
sb.delete(5, 14);
sb.deleteCharAt(int index);
sb.setCharAt(index, newChar);
int length = sb.length();
char ch = sb.charAt(0);
sb.reverse();
String result = sb.toString();
|
kmp算法跳过
4.3困难题目
5.栈与队列
5.1知识点
辅助栈(155)、
分数字栈和符号栈(150、394)
单调栈(例子4,2,0,3,2,5):求右边第一个比它大的元素——单调递减栈(从栈底到栈头);求右边第一个比它小的元素——单调递增栈、
优先队列、
单调队列:维护某个范围内的最值使用
5.2用法
栈的常用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
Deque<Character> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();
push();
pop();
isEmpty();
peek()
|
队列的常用法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
offer();
poll();
isEmpty();
peek();
offerLast();
offerFirst();
PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) {
return map.get(a) - map.get(b);
}
});
|
5.3困难题目
394.字符串解码、42.接雨水、239.滑动窗口最大值(单调队列)
6.二叉树
6.1知识点
递归三要素(1.确定参数和返回值。2.确定终止条件。3.确定单层递归的逻辑。)
各种遍历方式的非递归写法
各种遍历方式、各种遍历方式+双指针、各种遍历方式+全局变量
深度和高度:(高度和深度是相反的,求高度用后序遍历,求深度用前序遍历)
用回溯法求解二叉树问题(257.二叉树的所有路径)
DFS的应用(437.路径总和Ⅲ)
二叉搜索树(性质、搜索、插入(只往叶子节点插入)、删除(需要调整树的结构)、数组转二叉搜索树)
根据中序+前/后序数据构造二叉树问题:需要额外四个指针,指示两个数据的起点和终点。需要一个map存储一个数组中的元素在另一个数组中的下标位置。
6.2方法
层次遍历模板
6.3困难题目
543.二叉树的直径、450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点、669.修剪二叉搜索树、124.二叉树的最大路径和
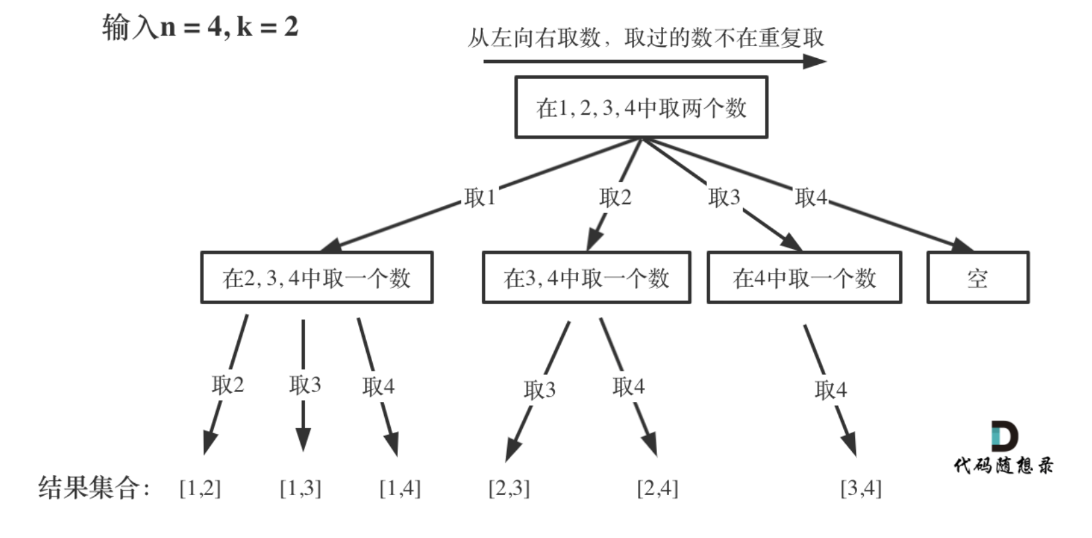
7.回溯
本质也是暴力搜索,但是在无法确定多少层for循环时使用
7.1知识点
树层去重:同一树层上不能取相同的元素
1
2
3
4
5
|
if(i>0 && used[i-1]==false && candidates[i-1]==candidates[i]){
continue;
}
|
树枝去重:同一树枝上不能取相同的元素
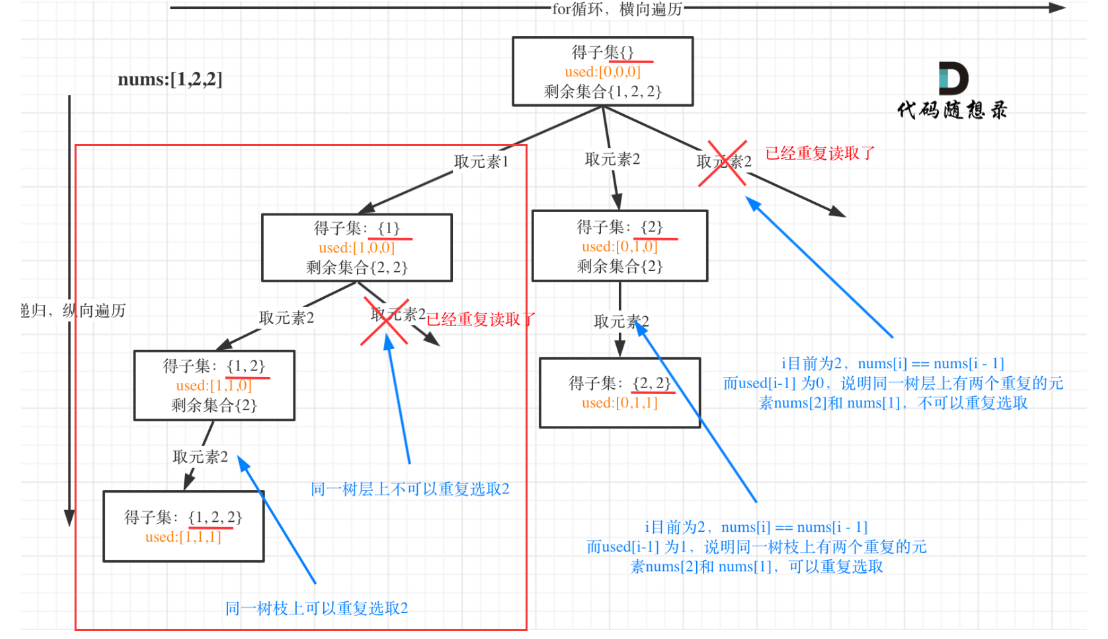
去重要借助used数组 + 对原始数组排序。
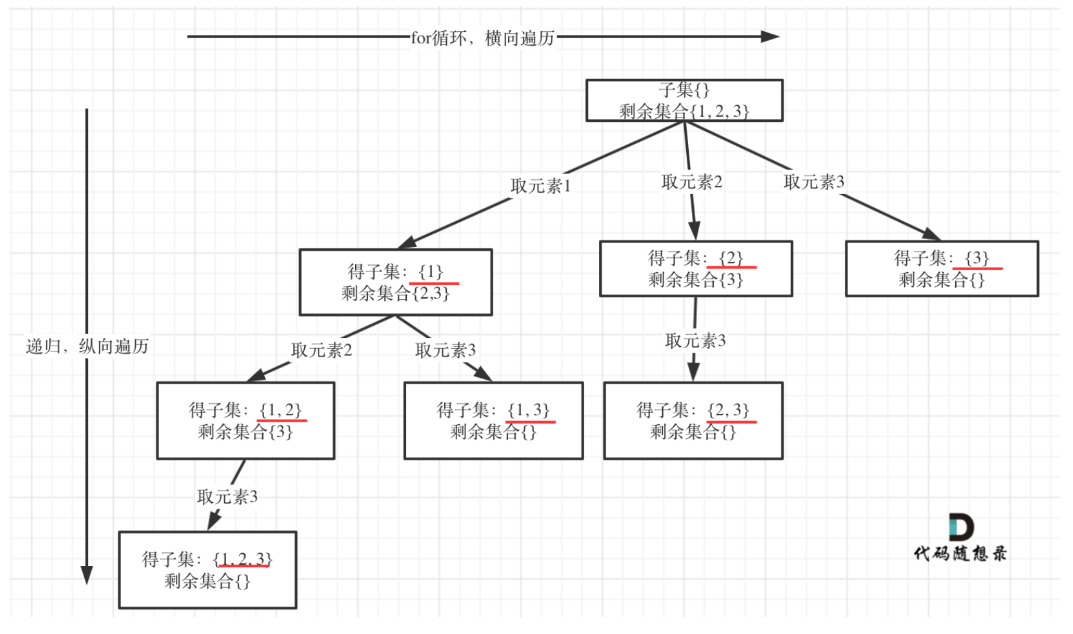
组合问题和分割问题都是收集树的叶子节点,而子集问题是找树的所有节点。
收集子集要放在终止条件上方,否则会漏掉。
使用used数组
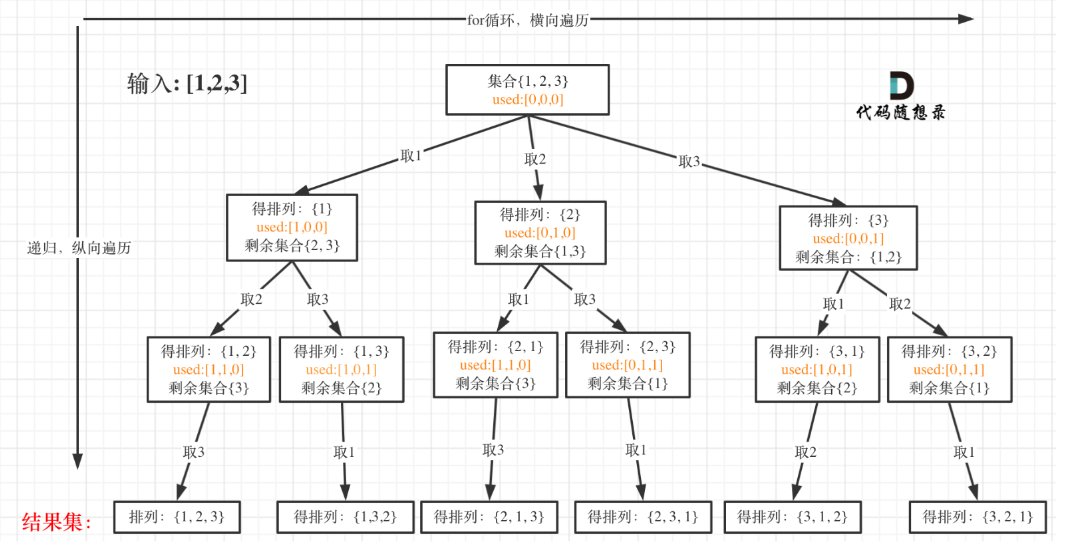
N皇后、解数独
dfs和回溯作比较:岛屿数量和单词搜索这两题。
7.2方法
模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| void backtracking(参数){
if(终止条件){
收集结果;
return;
}
for(集合元素){
处理节点;
递归函数;
回溯操作;
}
return;
}
1.递归函数参数和返回值:形参根据题目来定,返回值一般都是void
2.递归终止条件
3.单层搜索逻辑
|
辅助变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
|
7.3困难题目
40.组合总和Ⅱ、491.非递减子序列(不能排序的去重借助set去重)、51.N皇后(处理二维数组)
8.贪心
9.动态规划
初始化:递推公式没有考虑到的才需要初始化。
9.1知识点
问题分类
给了背包的容量,问能不能装满;
给了背包的容量,问最多能装多少价值;
给了背包的容量,有几种方法装满(递归公式不一样);
给了背包的容量,最多能装几个物品装满;
ps:可能递归公式不一样,但遍历顺序都一样。
递推公式
1.二维
需要二维数组 dp[i][j] : [0,i]物品任取放进容量为j的背包中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
for(int i = 1; i < weight.size(); i++) {
for(int j = 0; j <= bagweight; j++) {
if (j < weight[i]) dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j];
else dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i - 1][j - weight[i]] + value[i]);
}
}
两层for,先物品后容量或者先容量后物品,对于二维数组实现的0-1背包,顺序都可以。
可以看画表的遍历顺序确定。
|
2.一维数组
对二维数组的改进,直接把上一层拷贝到当前层
因为从右边开始才能保证你的dp[j-w[i]]这个是上一层的呀
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| for (int i = 0; i < wLen; i++){
for (int j = bagWeight; j >= weight[i]; j--){
dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]);
}
}
先物品后背包,不能颠倒;
且背包应该是倒叙遍历(倒叙保证了物品只被添加一次)。
|
同一件物品可以使用无数次;背包改为正序遍历。
1
2
3
4
5
6
| for (int i = 0; i < wLen; i++){
for(int j = weight[i]; j <= bagWeight; j++){
dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]);
}
}
|
根据不同题目,两层for循环的顺序会有所不同,先物品后背包对应组合问题,先背包后物品对应排序问题。
纯完全背包问题:两层for循环任意
组合问题:先物品后背包
排列问题:先背包后物品(可以剪枝)
二维dp问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
dp[i][0] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1] + prices[i], dp[i - 1][0]);
dp[i][1] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][1], -prices[i]);
dp[0][0] = 0;
dp[0][1] = -prices[0];
|
子序列(不连续)、子序列(连续)、二维子序列(二维dp)、编辑距离(难)、
回文:需要二维dp数组(boolean),i,j表示 i 到 j 范围内的子串是否是回文的;且遍历顺序有讲究。
借助两个dp[]数组共同实现。
9.2方法
动规五步曲:
- 确定dp数组以及下标的含义
- 确定递推公式
- dp数组如何初始化
- 确定遍历顺序
- 举例推导dp数组
9.3困难题
343.整数拆分、96.不同的二叉搜索树、213.打家劫舍Ⅱ、编辑距离所有题目、647.回文子串、516.最长回文子序列、123.买股票的最佳时机Ⅲ(状态增加)
10.图论
10.1知识点
DFS、BFS、拓扑排序、
邻接表表示(3067)、
并查集:
- 将两个元素添加到一个集合中。
- 判断两个元素在不在同一个集合。
10.2方法
DFS模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| void dfs(参数) {
if (终止条件) {
存放结果;
return;
}
for (选择:本节点所连接的其他节点) {
处理节点;
dfs(图,选择的节点);
回溯,撤销处理结果
}
}
|
DFS三步曲:
- 确认递归函数,参数
- 确认终止条件
- 处理目前搜索节点出发的路径
BFS模板
邻接表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| List<int[]>[] graph = new ArrayList[n];
Arrays.setAll(graph, i -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] e : edges) {
int u = e[0];
int v = e[1];
int w = e[2];
graph[u].add(new int[]{v, w});
graph[v].add(new int[]{u, w});
}
|
二分查找
74.搜索二维矩阵和240.搜索二维矩阵Ⅱ:(当每行元素为升序且每行的第一个整数大于前一行的最后一个整数时,可以使用两次二分查找找到任意一个元素;当只有行和列是升序时,无法使用两次二分)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
int low = 0;
int high = arr.length-1;
while (low <= high){
int mid = (low + high)/2;
if (arr[mid] < key){
low = mid + 1;
}else{
high = mid -1;
}
return low;
|
最终的结果:low的左侧都是low的满足判断条件的,high的右侧都是满足high的判断条件的。
当二分查找结束后,low = high + 1, low - 1指向的一定是 < target的数, high + 1 指向的一定是 > =target的数。
针对>,<,>=,<=的情况
大于:可以看作大于等于target+1的情况
小于:大于等于target的那个数左边的那个数
小于等于:大于target左边的那个数
34.当数组中有重复元素时,使用传统二分无法确定找到的是多个重复元素中的哪个。
数学
1
2
3
| private int gcd(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| boolean isPrime(int n) {
for (int i = 2; i * i <= n; i++) {
if (n % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return n >= 2;
}
|
位运算
1
2
|
int count = Integer.bitCount(num);
|
前缀和
一维前缀和
初始化:
定义preSum[0] = 0
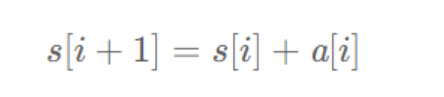
计算任意区间的和:
[left,right]区间的和为 : preSum[right + 1] - preSum[left]
二维前缀和
初始化二维前缀和

计算任意子矩阵元素和
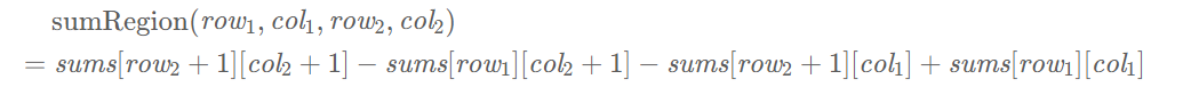
并查集
用于处理一些不相交集合的合并问题,即连通性问题。
针对无向图。
并查集我们一般用一维数组来记录,二维可以转化为一维。
并查集主要有两个功能:
- 将两个元素添加到一个集合中。
- 判断两个元素在不在同一个集合。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| class UnionFind {
int[] parents;
public UnionFind(int totalNodes) {
parents = new int[totalNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < totalNodes; i++) {
parents[i] = i;
}
}
void union(int node1, int node2) {
int root1 = find(node1);
int root2 = find(node2);
if (root1 != root2) {
parents[root2] = root1;
}
}
int find(int node) {
while (parents[node] != node) {
parents[node] = parents[parents[node]];
node = parents[node];
}
return node;
}
boolean isConnected(int node1, int node2) {
return find(node1) == find(node2);
}
}
|
题目
130、721
树状数组
相当于动态的前缀和,更新查询都是O(logn),克服了前缀和无法更新的缺点。
使用场景
五分钟丝滑动画讲解 | 树状数组_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
〔manim | 算法 | 数据结构〕 完全理解并深入应用树状数组 | 支持多种动态维护区间操作_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
蓝桥杯JAVA-12.树状数组模板(JAVA实现)_java 下载树形模板-CSDN博客
题目
3072、307
使用讲解
拆分[1,i]这个区间,按照二进制分解,13=8+4+1,拆分后形成[13,13] [9,12] [1,8]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
class BinaryIndexedTree {
private int[] tree;
public BinaryIndexedTree(int n) {
tree = new int[n + 1];
}
public void add(int i, int x) {
while (i < tree.length) {
tree[i] += x;
i += i & -i;
}
}
public int get(int i) {
int sum = 0;
while (i > 0) {
sum += tree[i];
i -= i & -i;
}
return sum;
}
}
|
剑指offer
287.寻找重复数287. 寻找重复数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
240.搜索二维矩阵240. 搜索二维矩阵 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
105.从前序和中序构造二叉树105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
232.用栈实现队列232. 用栈实现队列
509.斐波那契数509. 斐波那契数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
153.寻找旋转数组的最小值153. 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
79.单词搜索79. 单词搜索 - 力扣(LeetCode)
191.位1的个数191. 位1的个数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
50.Pow(x, n)50. Pow(x, n) - 力扣(LeetCode)
237.删除链表中的节点237. 删除链表中的节点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
82.删除链表中的重复元素82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
10.正则表达式匹配10. 正则表达式匹配 - 力扣(LeetCode)
65.有效数字65. 有效数字 - 力扣(LeetCode)
905.按奇偶排序数组905. 按奇偶排序数组 - 力扣(LeetCode)
19.删除链表的倒数第n个节点19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点 - 力扣(LeetCode)
142.环形链表Ⅱ142. 环形链表 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
206.反转链表206. 反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
21.合并两个有序数组21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
572.另一颗树的子树572. 另一棵树的子树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
226.翻转二叉树226. 翻转二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
101.对称二叉树101. 对称二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
54.螺旋矩阵54. 螺旋矩阵 - 力扣(LeetCode)
155.最小栈155. 最小栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
946.验证栈序列946. 验证栈序列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
102.二叉树的层序遍历
103.二叉树的锯齿形遍历103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)
113.路径总和113. 路径总和 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
138.随机链表的复制138. 随机链表的复制 - 力扣(LeetCode)
297.二叉树的序列化和反序列化297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化 - 力扣(LeetCode)
46.全排列46. 全排列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
47.全排列Ⅱ47. 全排列 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
77.组合77. 组合 - 力扣(LeetCode)
169.多数元素169. 多数元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
215.数组中第k大元素215. 数组中的第K个最大元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
295.数据流的中位数295. 数据流的中位数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
53.最大子数组和53. 最大子数组和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
233.数字1的个数233. 数字 1 的个数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
400.第n位数字400. 第 N 位数字 - 力扣(LeetCode)
179.最大数179. 最大数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
91.解码方法91. 解码方法 - 力扣(LeetCode)
64.最小路径和64. 最小路径和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
3.无重复字符的最长字串3. 无重复字符的最长子串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
264.丑数Ⅱ264. 丑数 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
387.字符串中的第一个唯一字符387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符 - 力扣(LeetCode)
493.翻转对493. 翻转对 - 力扣(LeetCode)
160.相交链表160. 相交链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
34.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置 - 力扣(LeetCode)
268.丢失的数字268. 丢失的数字 - 力扣(LeetCode)
230.二叉搜索树中第k小的元素230. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
104.二叉树的最大深度
110.平衡二叉树110. 平衡二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
260.只出现一次的数字Ⅲ260. 只出现一次的数字 III - 力扣(LeetCode)
137.只出现一次的数字Ⅱ137. 只出现一次的数字 II - 力扣(LeetCode)
167.两数之和Ⅱ167. 两数之和 II - 输入有序数组 - 力扣(LeetCode)
829.连续整数求和829. 连续整数求和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
151.反转字符串中的单词151. 反转字符串中的单词 - 力扣(LeetCode)
189.轮转数组189. 轮转数组 - 力扣(LeetCode)
239.滑动窗口最大值239. 滑动窗口最大值 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1155.掷骰子等于目标和的方法数1155. 掷骰子等于目标和的方法数
121.买卖股票的最佳时机121. 买卖股票的最佳时机 - 力扣(LeetCode)
技巧题目
异或
268、136
非常规题目
单例模式的手写
- 一个私有构造函数 (确保只能单例类自己创建实例)
- 一个私有静态变量 (确保只有一个实例)
- 一个公有静态函数 (给使用者提供调用方法)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
public class Singleton{
private static Singleton uniqueInstance;
private Singleton(){}
public static Singleton getUniqueInstance(){
if(uniqueInstance == null){
uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
}
return uniqueInstance;
}
}
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton uniqueInstance;
private static singleton() {
}
public static synchronized Singleton getUinqueInstance() {
if (uniqueInstance == null) {
uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
}
return uniqueInstance;
}
}
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getUniqueInstance() {
return uniqueInstance;
}
}
public class Singleton {
private volatile static Singleton uniqueInstance;
private Singleton() {
}
public static Singleton getUniqueInstance() {
if (uniqueInstance == null) {
synchronized (Singleton.class) {
if (uniqueInstance == null) {
uniqueInstance = new Singleton();
}
}
}
return uniqueInstance;
}
}
|
排序算法
线程池的使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public static void fixedThreadPool() {
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("任务被执行,线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
};
threadPool.submit(runnable);
}
threadPool.shutdown();
|
多线程的使用
八个经典的java多线程编程题目_java线程题目-CSDN博客
多线程轮流输出26个字母怎么实现?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| public class Main {
private static final int CHARACTER_COUNT = 26;
private static volatile int currentIndex = 0;
private static final int THREAD_COUNT = 5;
private static final Object LOCK = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_COUNT; i++) {
String threadName = "thread_" + i;
new Thread(new PrintThread(threadName, i)).start();
}
}
static class PrintThread implements Runnable {
private final String threadName;
private final int threadNumber;
public PrintThread(String threadName, int threadNumber) {
this.threadName = threadName;
this.threadNumber = threadNumber;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (currentIndex < CHARACTER_COUNT) {
if (currentIndex % THREAD_COUNT == threadNumber) {
synchronized (LOCK) {
if (currentIndex < CHARACTER_COUNT) {
System.out.println(threadName + "_print_:" + (char) (97 + currentIndex));
currentIndex++;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
|
不使用锁呢?
死锁
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| public class DeadLockDemo {
private static Object resource1 = new Object();
private static Object resource2 = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (resource1) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get resource1");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "waiting get resource2");
synchronized (resource2) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get resource2");
}
}
}, "线程 1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
synchronized (resource2) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get resource2");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "waiting get resource1");
synchronized (resource1) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + "get resource1");
}
}
}, "线程 2").start();
}
}
|
ACM模式
面试 | Java 算法的 ACM 模式_java acm模式-CSDN博客